用户认证流程
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
我们直接来看UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter类,
1 | public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends |
在attemptAuthentication()方法中:主要是先进行请求判断并获取username和password的值,然后再生成一个UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken对象,将这个对象塞进AuthenticationManager对象并返回,注意:此时的authRequest的权限是没有任何值的。
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
不过我们可以先看看UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken的构造方法:
1 | public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials) { |
其实UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken是继承于Authentication,该对象在学习笔记一中的中”自定义处理登录成功/失败”章节里的自定义登录成功里有提到过,它是处理登录成功回调方法中的一个参数,里面包含了用户信息、请求信息等参数。
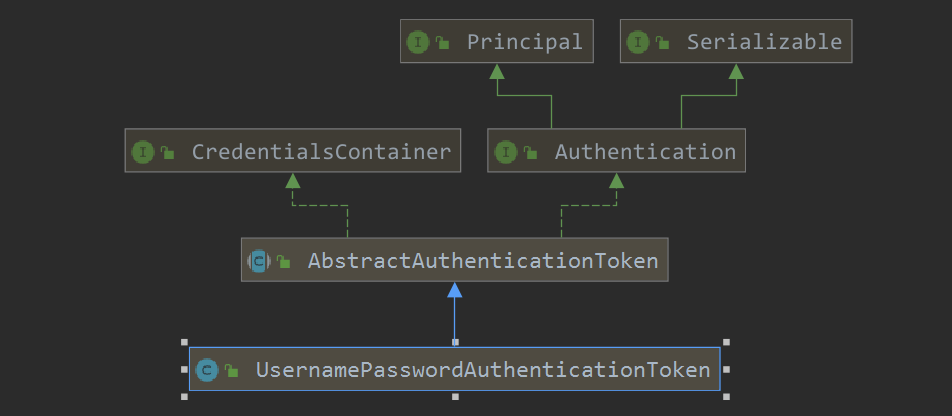
来一张继承关系图,对其有个大概的认识,注意到Authentication继承了Principal。
AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager是一个接口,它的所有实现类如图:
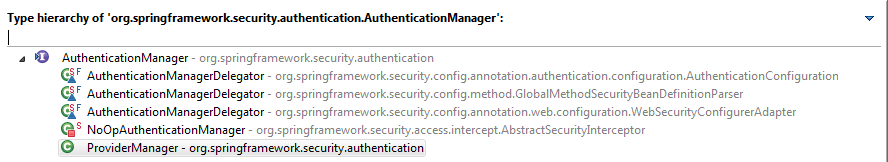
其中一个十分核心的类就是:ProviderManager,在attemptAuthentication()方法最后返回的就是这个类
1 | this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest); |
进入authenticate()方法查看具体做了什么:
1 | public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) |
这里首先通过 provider 判断是否支持当前传入进来的Authentication,目前我们使用的是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,因为除了帐号密码登录的方式,还会有其他的方式,比如JwtAuthenticationToken。
从整体来看Authentication 的实现类如图:
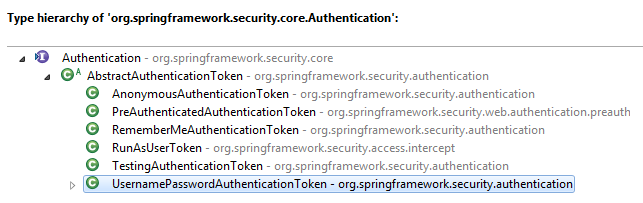
官方 API 文档列出了所有的子类
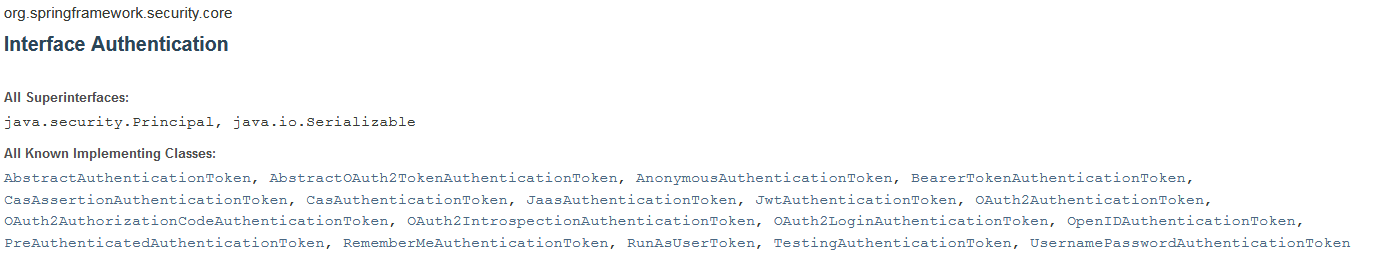
从整体来看AuthenticationProvider的实现类如图:
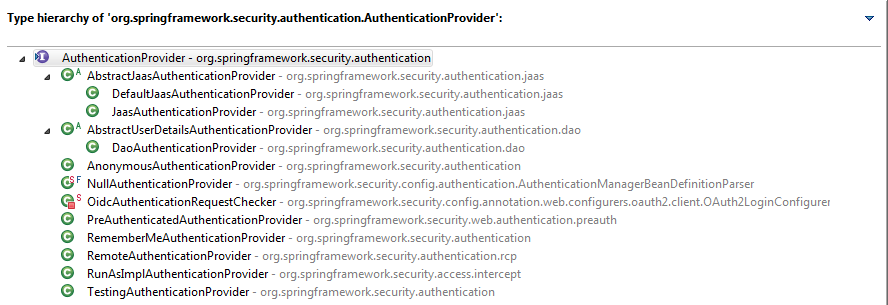
官方 API 文档列出了所有的子类
根据我们目前所使用的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,provider 对应的是AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider抽象类的子类DaoAuthenticationProvider,其authenticate()属于抽象类本身的方法。
1 | public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) |
注意:retrieveUser()的具体方法实现是由DaoAuthenticationProvider类完成的:
1 | public class DaoAuthenticationProvider extends AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider { |
同时createSuccessAuthentication()的方法也是由DaoAuthenticationProvider类来完成的:
1 | // 子类拿 user 对象 |
小结:authenticate()的认证逻辑
- 去调用自己实现的
UserDetailsService,返回UserDetails - 对 UserDetails 的信息进行校验,主要是帐号是否被冻结,是否过期等
- 对密码进行检查,这里调用了
PasswordEncoder,检查 UserDetails 是否可用。 - 返回经过认证的
Authentication
编码技巧提示:这里在认证之前使用了
Assert.isInstanceOf()进行断言校验,方法内部也不断用了Assert.notNull(),这种编码非常的灵巧,省去了后续的类型判断。
这里的两次对UserDetails的检查,主要就是通过它的四个返回 boolean 类型的方法(isAccountNonExpired(),isAccountNonLocked(),isCredentialsNonExpired(),isEnabled())。
经过信息的校验之后,通过UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken的全参构造方法,返回了一个已经过认证的Authentication。
拿到经过认证的Authentication之后,至此UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter的过滤步骤就完全结束了,之后就会进入BasicAuthenticationFilter,具体来说就是去调用successHandler。或者未通过认证,去调用failureHandler。
已认证数据共享
完成了用户认证处理流程之后,我们思考一下是如何在多个请求之间共享这个认证结果的呢?因为没有做关于这方面的配置,所以可以联想到默认的方式应该是在session中存入了认证结果。思考:那么是什么时候存放入session中的呢?
认证流程完毕之后,再看是谁调用的它,发现是AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter的doFilter()进行调用的,这是AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter继承关系结构图:
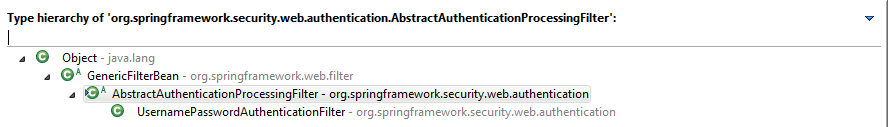
当认证成功之后会调用successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult),该方法中,不仅调用了successHandler,还有一行比较重要的代码:
1 | public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter extends GenericFilterBean |
SecurityContextHolderStrategy接口的所有实现类:
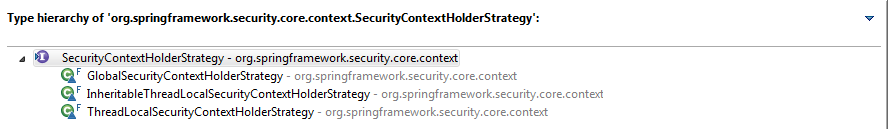
非常显眼的看出:ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy类:
1 | final class ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy implements |
注意:
SecurityContext类的equals()和hashCode()方法已经重写了,用来保证了authentication的唯一性。
身份认证成功后,最后在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter返回后会进入一个AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter类中调用successfulAuthentication()方法,这个方法最后会返回我们自己定义的登录成功处理器handler。
在返回之前,它会调用SecurityContext,最后将认证的结果放入SecurityContextHolder中,SecurityContext 类很简单,重写了equals() 方法和hashCode()方法,保证了authentication的唯一性。
从代码可以看出:SecurityContextHolder类实际上是对ThreadLocal的一个封装,可以在不同方法之间进行通信,可以简单理解为线程级别的一个全局变量。
因此,可以在同一个线程中的不同方法中获取到认证信息。最后会被SecurityContextPersistenceFilter过滤器使用,这个过滤器的作用是:
当一个请求来的时候,它会将 session 中的值传入到该线程中,当请求返回的时候,它会判断该请求线程是否有 SecurityContext,如果有它会将其放入到 session 中,因此保证了请求结果可以在不同的请求之间共享。
用户认证流程总结
引用徐靖峰在个人博客Spring Security(一)–Architecture Overview中的概括性总结,非常的到位:
- 用户名和密码被过滤器获取到,封装成
Authentication,通常情况下是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken这个实现类。 AuthenticationManager身份管理器负责验证这个Authentication。- 认证成功后,
AuthenticationManager身份管理器返回一个被填充满了信息的(包括上面提到的权限信息,身份信息,细节信息,但密码通常会被移除)Authentication实例。 SecurityContextHolder安全上下文容器将第3步填充了信息的Authentication,通过SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(…)方法,设置到其中。
高度概括起来本章节所有用的核心认证相关接口:SecurityContextHolder是
身份信息的存放容器,Authentication是身份信息的抽象,AuthenticationManager是身份认证器,一般常用的是用户名+密码的身份认证器,还有其它认证器,如邮箱+密码、手机号码+密码等。
再引用一张十分流行的流程图来表示用户的认证过程:
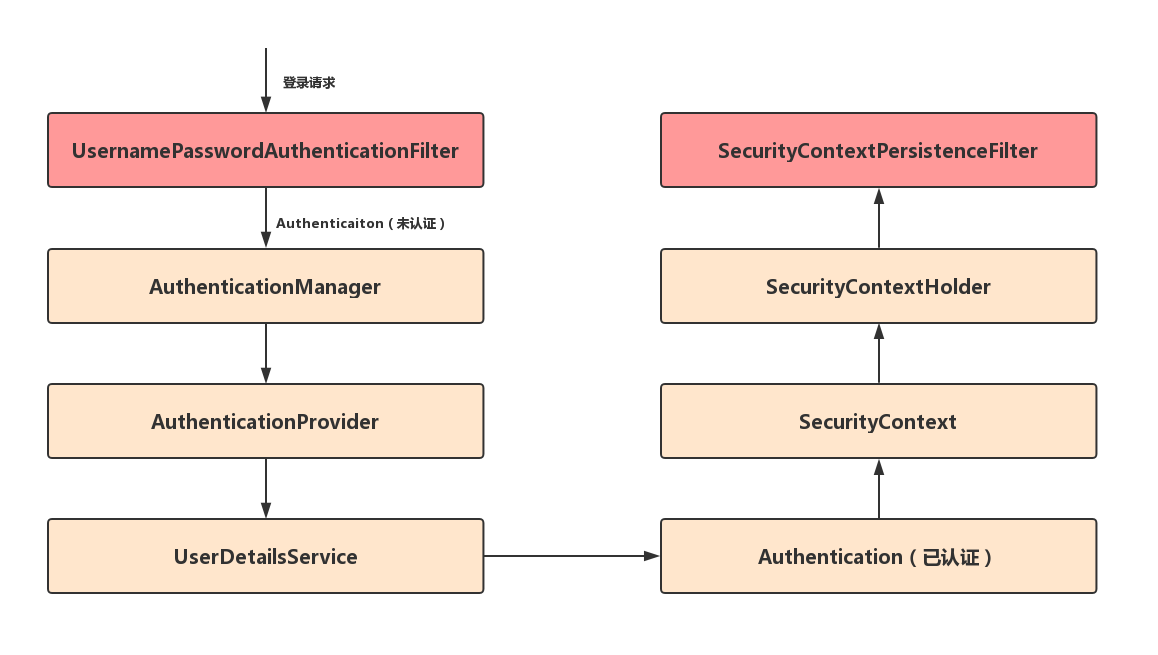
架构概览图
为了更加形象的理解,在徐靖峰大佬的经典架构图之上,根据自己的理解,做了更多的细化和调整:
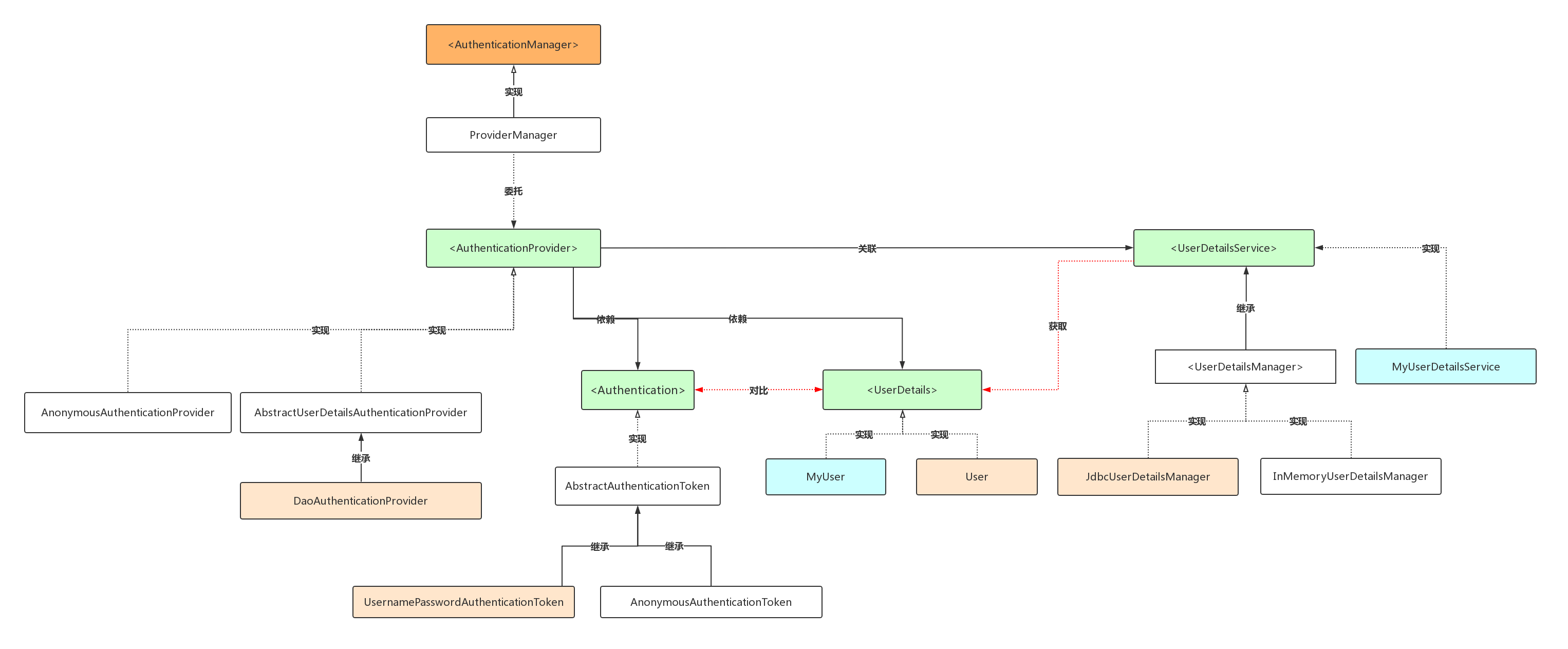
获取认证用户信息
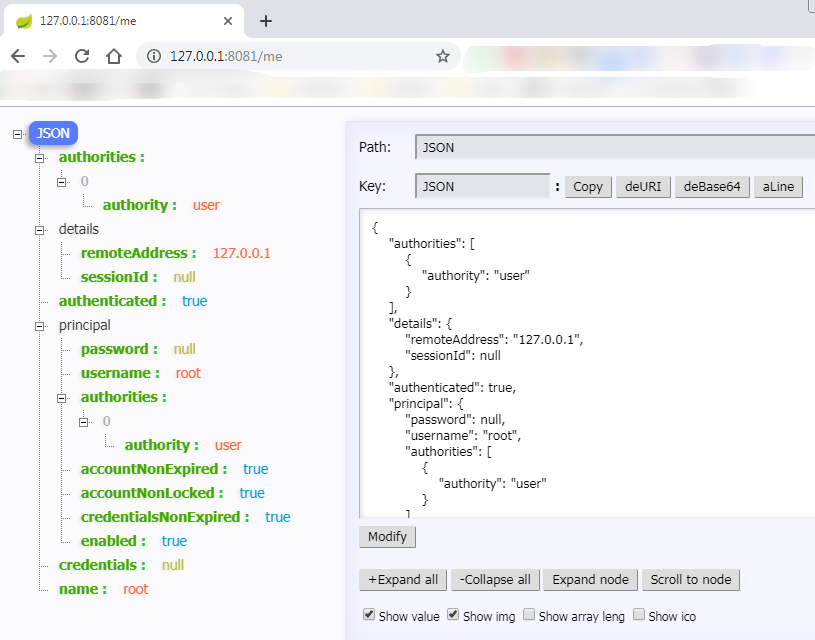
如果我们需要获取用的校验过的所有信息,该如何获取呢?上面我们知道了会将校验结果放入 session 中,因此,我们可以通过 session 获取:
1 |
|
在登录成功之后,上面有两种方式来获取,访问上面的请求,就会获取用户全部的校验信息,包括ip地址等信息。
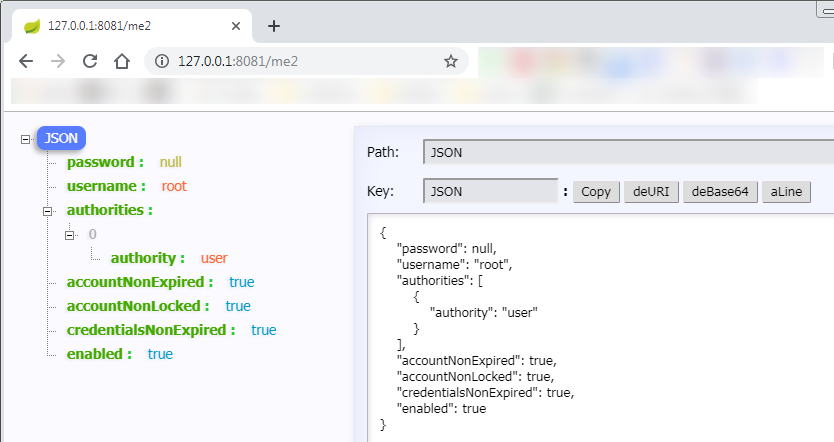
如果我们只想获取用户名和密码以及它的权限,不需要ip地址等太多的信息可以使用下面的方式来获取信息:
1 |
|
参考资料:
https://www.cnkirito.moe/spring-security-1/
